01-Propositional_Logic
I Introduction
I.1 base notations
Our first building block is the notion of a proposition, which is simply a statement which is either true or false.
For example:

Notations we should know:
- Conjunction(合取): P∧Q (“P and Q”). True only when both P and Q are true.
- Disjunction(析取): P∨Q (“P or Q”). True when at least one of P and Q is true.
- Negation(取反/否): ¬P (“not P”). True when P is false.
- Implication(蕴涵词): P ⇒ Q (“P implies Q”). This is the same as “If P, then Q.”**
- two-way implication p↔q
(Detailed reason omission)
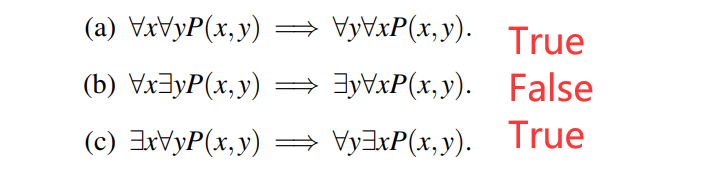
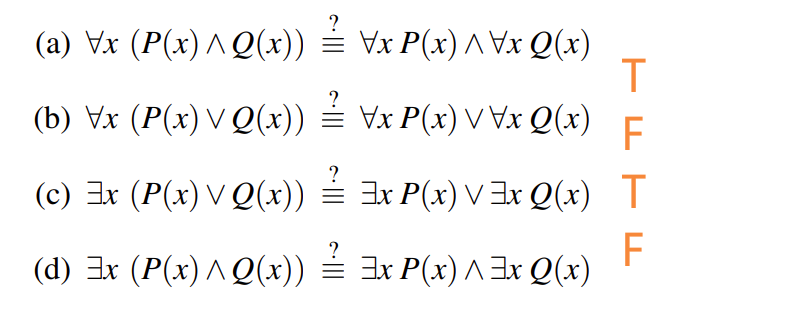
- quantifiers: The universal quantifier ∀ (“for all”) and the existential quantifier ∃ (“there exists”).
We often write a proposition in the form of something like (∀x ∈ Z)(∃y ∈ Z)(x < y)
- equivalent is something like:
- ¬(P∧Q) ≡ (¬P∨ ¬Q)
- ¬(P∨Q) ≡ (¬P∧ ¬Q)
Of course, these two formulas should be remembered since they tell us how to negate conjunctions and disjunctions
- about P→Q, the truth table is shown below:(
0stands for F while1stands for T)
| P | Q | P→Q |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
- about P↔Q, the truth table is shown below:(
0stands for F while1stands for T)
| P | Q | P↔Q |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
- We say that a sentence A entails another sentence B if in all models that A is true, B is as well, and we represent this relationship as A ⊨ B.
I.2 proposition formula





(穷举定理我们在Proof by Cases(案例证明)中将会使用到)
I.3 logical equivalence
当命题
实际上,符号 ⊨ 也是,但是打不出来,所以一般用
逻辑等价:任何赋值情况下,A 和 B 都等值。
I.3.1 important logical equivalence


I.4 logical implication
当命题公式 A
公式 A 的所有成真赋值都是公式 B 的成真赋值。
即任何赋值情况下,只要 A 为真,则 B 为真;
I.4.1 important logical implication

I.5 The important properties of logical equivalence and logical implication

I.6 ways to proof

I.7 priority of operations
1. 括号 ():无论在哪个领域,括号始终具有最高的优先级,用于改变默认的优先级顺序。
2. 非 ~ !:在逻辑运算中,否定(逻辑非、位非)通常具有较高的优先级。
3. 与 ∧:这包括逻辑与(AND)、位与(&)。在没有括号改变顺序的情况下,它们通常在否定之后立即评估。
4. 异或 ⊕:在某些情况下,需要考虑异或运算(XOR),它可能在与运算和或运算之间。
5. 或 ∨:这包括逻辑或(OR)、位或(|)。它们在逻辑与之后进行评估。
6. 条件 →:如蕴含(→)通常优先级较低。
7. 双条件↔:双条件(↔)通常具有最低的优先级
II signs in latex
| 符号 | ¬ | ∧ | ∨ | → | ↔ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| latex 公式 | \neg | \wedge | \vee | \to | \leftrightarrow |
III Practice
We need a lot of insight into propositions rather than just grasping concepts
For every real number k, there is a unique real solution to
= k.
(∀k ∈ R) (∃x ∈ R)(x 3 = k)∧(∀y,z ∈ R)(((y 3 = k)∧(z 3 = k)) ⇒ (y = z)) .